
2025-01-30 14:37
IndustryLeverage and Margin in Forex.
#firstdealofthenewyearAKEEL
Leverage and margin are two key concepts in forex trading that allow traders to control larger positions with a smaller amount of capital. While leverage increases potential profits, it also magnifies potential losses, making risk management crucial.
1. What is Leverage?
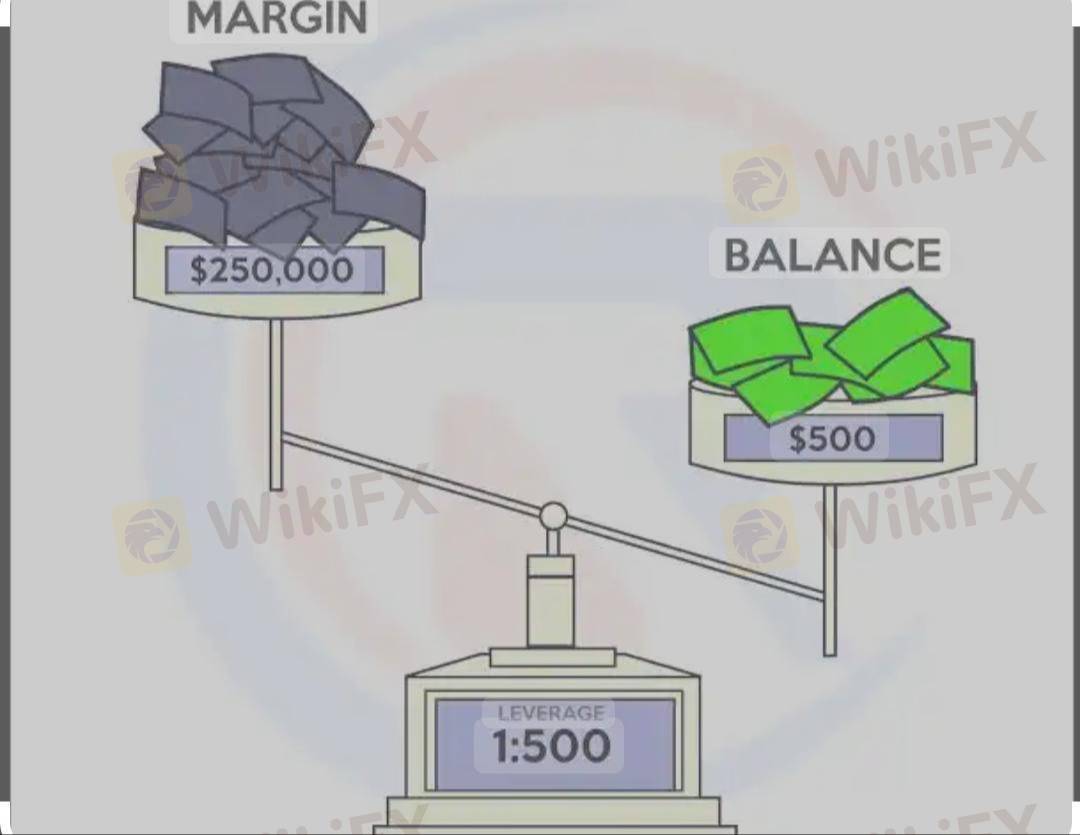
Leverage is the ability to control a large position in the forex market with a small amount of capital. It is expressed as a ratio, such as 50:1, 100:1, or 500:1, depending on the broker and regulations.
Example of Leverage:
Suppose you have $1,000 in your trading account.
With 100:1 leverage, you can control $100,000 worth of a currency pair.
If the price moves in your favor by 1%, your profit would be $1,000 (100% of your capital).
However, if the price moves against you by 1%, you could lose $1,000 and wipe out your account.
Higher leverage = higher profit potential but also higher risk.
2. What is Margin?
Margin is the amount of money required to open and maintain a leveraged position. It is expressed as a percentage of the total trade size.
Types of Margin:
Required Margin: The initial deposit needed to open a position.
Used Margin: The total margin currently used for all open trades.
Free Margin: The remaining balance available to open new trades.
Margin Level: The percentage of equity compared to used margin. If it drops too low, you may receive a margin call.
Example of Margin:
If your broker requires a 1% margin to open a trade:
To control $100,000 with 100:1 leverage, you need $1,000.
To control $50,000 with 50:1 leverage, you need $1,000.
3. Margin Call and Stop Out Level
A margin call occurs when your account balance falls below the required margin level. Your broker may ask you to deposit more funds.
A stop-out level is the point at which the broker automatically closes your trades to prevent further losses.
4. Leverage & Margin Risk Management
Use Stop-Loss Orders: Set limits on losses to prevent wiping out your account.
Avoid Over-Leveraging: A high leverage ratio can lead to quick losses.
Monitor Margin Level: Keep an eye on margin usage to avoid margin calls.
Trade with a Risk Management Strategy: Never risk more than 1-2% of your capital per trade.
Conclusion
Leverage can be a powerful tool in forex trading, but it comes with increased risk. Properly understanding and managing margin is crucial to avoiding margin calls and preserving your capital. Always use risk management strategies to trade safely.
Would you like more details on any part?
#firstdealofthenewyearAKEEL
Like 0
belloyauyahayya
Trader
Hot content
Industry
Event-A comment a day,Keep rewards worthy up to$27
Industry
Nigeria Event Giveaway-Win₦5000 Mobilephone Credit
Industry
Nigeria Event Giveaway-Win ₦2500 MobilePhoneCredit
Industry
South Africa Event-Come&Win 240ZAR Phone Credit
Industry
Nigeria Event-Discuss Forex&Win2500NGN PhoneCredit
Industry
[Nigeria Event]Discuss&win 2500 Naira Phone Credit
Forum category

Platform

Exhibition

Agent

Recruitment

EA

Industry

Market

Index
Leverage and Margin in Forex.
 Hong Kong | 2025-01-30 14:37
Hong Kong | 2025-01-30 14:37#firstdealofthenewyearAKEEL
Leverage and margin are two key concepts in forex trading that allow traders to control larger positions with a smaller amount of capital. While leverage increases potential profits, it also magnifies potential losses, making risk management crucial.
1. What is Leverage?
Leverage is the ability to control a large position in the forex market with a small amount of capital. It is expressed as a ratio, such as 50:1, 100:1, or 500:1, depending on the broker and regulations.
Example of Leverage:
Suppose you have $1,000 in your trading account.
With 100:1 leverage, you can control $100,000 worth of a currency pair.
If the price moves in your favor by 1%, your profit would be $1,000 (100% of your capital).
However, if the price moves against you by 1%, you could lose $1,000 and wipe out your account.
Higher leverage = higher profit potential but also higher risk.
2. What is Margin?
Margin is the amount of money required to open and maintain a leveraged position. It is expressed as a percentage of the total trade size.
Types of Margin:
Required Margin: The initial deposit needed to open a position.
Used Margin: The total margin currently used for all open trades.
Free Margin: The remaining balance available to open new trades.
Margin Level: The percentage of equity compared to used margin. If it drops too low, you may receive a margin call.
Example of Margin:
If your broker requires a 1% margin to open a trade:
To control $100,000 with 100:1 leverage, you need $1,000.
To control $50,000 with 50:1 leverage, you need $1,000.
3. Margin Call and Stop Out Level
A margin call occurs when your account balance falls below the required margin level. Your broker may ask you to deposit more funds.
A stop-out level is the point at which the broker automatically closes your trades to prevent further losses.
4. Leverage & Margin Risk Management
Use Stop-Loss Orders: Set limits on losses to prevent wiping out your account.
Avoid Over-Leveraging: A high leverage ratio can lead to quick losses.
Monitor Margin Level: Keep an eye on margin usage to avoid margin calls.
Trade with a Risk Management Strategy: Never risk more than 1-2% of your capital per trade.
Conclusion
Leverage can be a powerful tool in forex trading, but it comes with increased risk. Properly understanding and managing margin is crucial to avoiding margin calls and preserving your capital. Always use risk management strategies to trade safely.
Would you like more details on any part?
#firstdealofthenewyearAKEEL
Like 0
I want to comment, too
Submit
0Comments

There is no comment yet. Make the first one.
Submit
There is no comment yet. Make the first one.