
2025-02-13 17:07
IndustrySupply chain disruptions
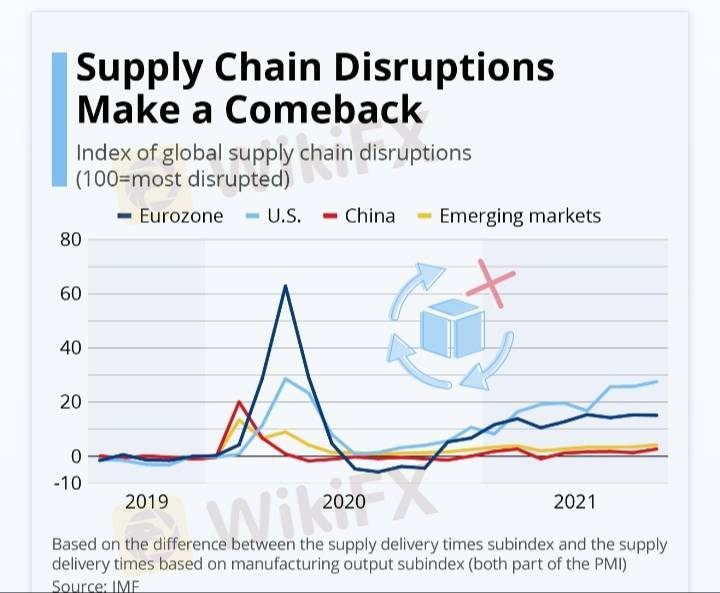
Supply chain disruptions can have significant economic effects across industries, influencing inflation, production costs, employment, and overall economic growth. Here are some key economic impacts:
1. Inflationary Pressures
When supply chains are disrupted, shortages of goods and raw materials occur, leading to increased prices.
Higher transportation and logistics costs due to delays and rerouting contribute to inflation.
Businesses pass these costs onto consumers, reducing purchasing power.
2. Reduced Economic Growth
Manufacturing slowdowns and reduced availability of critical components (e.g., semiconductors, energy, food) lower production output.
Delays in product availability affect GDP growth as consumer spending and business investments decline.
Global trade is impacted as exports and imports are delayed or restricted.
3. Business Losses and Closures
Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) with limited resources struggle to absorb increased costs and may shut down.
Larger corporations face revenue losses due to production halts and supply shortages.
Just-in-time (JIT) inventory strategies are disrupted, forcing companies to reconsider supply chain resilience.
4. Job Losses and Labor Market Instability
Factory closures and reduced production lead to layoffs in affected industries.
Supply chain disruptions in agriculture and food production impact farm workers and supply chain employees.
The logistics sector (truck drivers, warehouse workers, shipping industry) faces fluctuations in demand, affecting employment stability.
5. Financial Market Volatility
Stock prices of companies reliant on global supply chains become volatile.
Investors react to supply chain risks by adjusting portfolios, causing fluctuations in financial markets.
Central banks may adjust monetary policies (interest rates, stimulus measures) to counter economic downturns caused by disruptions.
6. Shift in Global Trade and Production Strategies
Countries and companies diversify suppliers to reduce dependency on single regions (e.g., China’s dominance in manufacturing).
There is increased investment in local production and reshoring (bringing manufacturing back home).
Digital transformation and automation investments increase to make supply chains more resilient.
Recent Examples of Supply Chain Disruptions and Their Economic Effects
COVID-19 Pandemic: Factory shutdowns, labor shortages, and port congestion led to global inflation and reduced economic growth.
Russia-Ukraine War: Energy and food supply disruptions led to increased fuel and grain prices, impacting global economies.
Suez Canal Blockage (2021): A single ship blockage delayed global trade worth billions, affecting industries worldwide.
#firstdealofthenewyearstylz
Like 0

BamiCreative
Broker
Hot content
Industry
Event-A comment a day,Keep rewards worthy up to$27
Industry
Nigeria Event Giveaway-Win₦5000 Mobilephone Credit
Industry
Nigeria Event Giveaway-Win ₦2500 MobilePhoneCredit
Industry
South Africa Event-Come&Win 240ZAR Phone Credit
Industry
Nigeria Event-Discuss Forex&Win2500NGN PhoneCredit
Industry
[Nigeria Event]Discuss&win 2500 Naira Phone Credit
Forum category

Platform

Exhibition

Agent

Recruitment

EA

Industry

Market

Index
Supply chain disruptions
 Hong Kong | 2025-02-13 17:07
Hong Kong | 2025-02-13 17:07Supply chain disruptions can have significant economic effects across industries, influencing inflation, production costs, employment, and overall economic growth. Here are some key economic impacts:
1. Inflationary Pressures
When supply chains are disrupted, shortages of goods and raw materials occur, leading to increased prices.
Higher transportation and logistics costs due to delays and rerouting contribute to inflation.
Businesses pass these costs onto consumers, reducing purchasing power.
2. Reduced Economic Growth
Manufacturing slowdowns and reduced availability of critical components (e.g., semiconductors, energy, food) lower production output.
Delays in product availability affect GDP growth as consumer spending and business investments decline.
Global trade is impacted as exports and imports are delayed or restricted.
3. Business Losses and Closures
Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) with limited resources struggle to absorb increased costs and may shut down.
Larger corporations face revenue losses due to production halts and supply shortages.
Just-in-time (JIT) inventory strategies are disrupted, forcing companies to reconsider supply chain resilience.
4. Job Losses and Labor Market Instability
Factory closures and reduced production lead to layoffs in affected industries.
Supply chain disruptions in agriculture and food production impact farm workers and supply chain employees.
The logistics sector (truck drivers, warehouse workers, shipping industry) faces fluctuations in demand, affecting employment stability.
5. Financial Market Volatility
Stock prices of companies reliant on global supply chains become volatile.
Investors react to supply chain risks by adjusting portfolios, causing fluctuations in financial markets.
Central banks may adjust monetary policies (interest rates, stimulus measures) to counter economic downturns caused by disruptions.
6. Shift in Global Trade and Production Strategies
Countries and companies diversify suppliers to reduce dependency on single regions (e.g., China’s dominance in manufacturing).
There is increased investment in local production and reshoring (bringing manufacturing back home).
Digital transformation and automation investments increase to make supply chains more resilient.
Recent Examples of Supply Chain Disruptions and Their Economic Effects
COVID-19 Pandemic: Factory shutdowns, labor shortages, and port congestion led to global inflation and reduced economic growth.
Russia-Ukraine War: Energy and food supply disruptions led to increased fuel and grain prices, impacting global economies.
Suez Canal Blockage (2021): A single ship blockage delayed global trade worth billions, affecting industries worldwide.
#firstdealofthenewyearstylz
Like 0
I want to comment, too
Submit
0Comments

There is no comment yet. Make the first one.
Submit
There is no comment yet. Make the first one.