
2025-02-16 06:59
IndustryCentral Bank Intervention in Forex Markets
#firstdealoftheneeyearastylz
Central bank intervention in Forex markets refers to the actions taken by a central bank to influence the value of its currency on the foreign exchange market. Here's an overview:
Types of Central Bank Intervention:
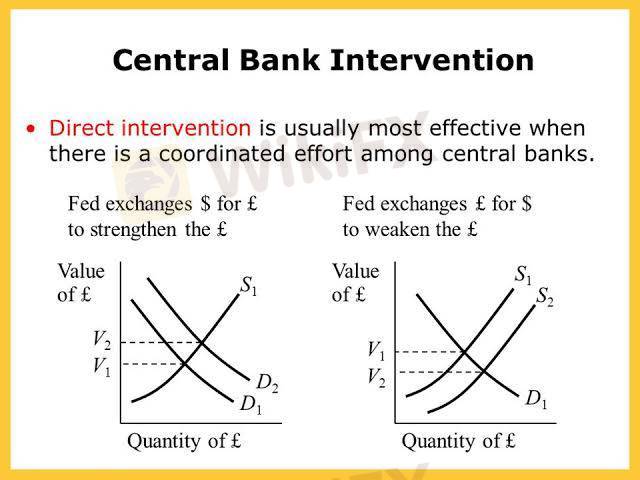
1. Direct Intervention: Buying or selling currencies directly on the Forex market to influence exchange rates.
2. Indirect Intervention: Using monetary policy tools, such as interest rates or reserve requirements, to influence exchange rates.
3. Verbal Intervention: Making public statements to influence market expectations and exchange rates.
Reasons for Central Bank Intervention:
1. Maintaining Exchange Rate Stability: To prevent excessive currency fluctuations that could harm the economy.
2. Controlling Inflation: To prevent high inflation by limiting the amount of currency in circulation.
3. Supporting Economic Growth: To boost exports and economic growth by maintaining a competitive exchange rate.
4. Managing Capital Flows: To regulate the flow of capital into or out of the country.
Tools Used for Central Bank Intervention:
1. Foreign Exchange Reserves: Central banks use their foreign exchange reserves to buy or sell currencies.
2. Interest Rates: Central banks adjust interest rates to influence exchange rates.
3. Forward Contracts: Central banks use forward contracts to buy or sell currencies at a set price.
4. Verbal Intervention: Central banks make public statements to influence market expectations.
Examples of Central Bank Intervention:
1. Swiss National Bank's intervention in 2011 to weaken the Swiss franc.
2. Bank of Japan's intervention in 2013 to weaken the Japanese yen.
3. European Central Bank's intervention in 2015 to weaken the euro.
Impact of Central Bank Intervention:
1. Short-term exchange rate stability.
2. Influence on market expectations.
3. Potential for long-term economic benefits.
4. Risk of market distortion and unintended consequences.
Limitations of Central Bank Intervention:
1. Limited resources: Central banks have limited foreign exchange reserves.
2. Market forces: Central banks may struggle to influence exchange rates in the face of strong market forces.
3. Unintended consequences: Intervention can lead to unintended consequences, such as market distortion.
Like 0

Odogwu920
Broker
Hot content
Industry
Event-A comment a day,Keep rewards worthy up to$27
Industry
Nigeria Event Giveaway-Win₦5000 Mobilephone Credit
Industry
Nigeria Event Giveaway-Win ₦2500 MobilePhoneCredit
Industry
South Africa Event-Come&Win 240ZAR Phone Credit
Industry
Nigeria Event-Discuss Forex&Win2500NGN PhoneCredit
Industry
[Nigeria Event]Discuss&win 2500 Naira Phone Credit
Forum category

Platform

Exhibition

Agent

Recruitment

EA

Industry

Market

Index
Central Bank Intervention in Forex Markets
 Hong Kong | 2025-02-16 06:59
Hong Kong | 2025-02-16 06:59#firstdealoftheneeyearastylz
Central bank intervention in Forex markets refers to the actions taken by a central bank to influence the value of its currency on the foreign exchange market. Here's an overview:
Types of Central Bank Intervention:
1. Direct Intervention: Buying or selling currencies directly on the Forex market to influence exchange rates.
2. Indirect Intervention: Using monetary policy tools, such as interest rates or reserve requirements, to influence exchange rates.
3. Verbal Intervention: Making public statements to influence market expectations and exchange rates.
Reasons for Central Bank Intervention:
1. Maintaining Exchange Rate Stability: To prevent excessive currency fluctuations that could harm the economy.
2. Controlling Inflation: To prevent high inflation by limiting the amount of currency in circulation.
3. Supporting Economic Growth: To boost exports and economic growth by maintaining a competitive exchange rate.
4. Managing Capital Flows: To regulate the flow of capital into or out of the country.
Tools Used for Central Bank Intervention:
1. Foreign Exchange Reserves: Central banks use their foreign exchange reserves to buy or sell currencies.
2. Interest Rates: Central banks adjust interest rates to influence exchange rates.
3. Forward Contracts: Central banks use forward contracts to buy or sell currencies at a set price.
4. Verbal Intervention: Central banks make public statements to influence market expectations.
Examples of Central Bank Intervention:
1. Swiss National Bank's intervention in 2011 to weaken the Swiss franc.
2. Bank of Japan's intervention in 2013 to weaken the Japanese yen.
3. European Central Bank's intervention in 2015 to weaken the euro.
Impact of Central Bank Intervention:
1. Short-term exchange rate stability.
2. Influence on market expectations.
3. Potential for long-term economic benefits.
4. Risk of market distortion and unintended consequences.
Limitations of Central Bank Intervention:
1. Limited resources: Central banks have limited foreign exchange reserves.
2. Market forces: Central banks may struggle to influence exchange rates in the face of strong market forces.
3. Unintended consequences: Intervention can lead to unintended consequences, such as market distortion.
Like 0
I want to comment, too
Submit
0Comments

There is no comment yet. Make the first one.
Submit
There is no comment yet. Make the first one.