
2025-02-14 19:41
इंडस्ट्रीBehavioral Finance: Psychology and Decision-Making
#Firstdealofthenewyearastylz
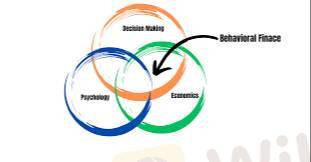
Behavioral finance is a field that blends psychology with finance to understand how individuals and markets behave irrationally. Traditional finance assumes that investors are rational and make decisions based on all available information to maximize wealth. However, behavioral finance recognizes that psychological biases, emotions, and cognitive errors often lead to irrational financial choices.
---
Key Areas of Behavioral Finance
1. Cognitive Biases in Financial Decision-Making
Cognitive biases are systematic patterns of deviation from rationality in judgment.
Overconfidence Bias – Investors overestimate their ability to predict market movements, leading to excessive trading.
Loss Aversion – The pain of losing money is psychologically stronger than the joy of gaining it, causing risk-averse behavior.
Confirmation Bias – Investors seek information that supports their existing beliefs and ignore contradictory data.
Anchoring Bias – Decisions are influenced by irrelevant reference points, such as past stock prices.
Availability Bias – Investors give more weight to recent or easily recalled events, impacting risk perception.
---
2. Emotional Influences on Investment Behavior
Emotions play a significant role in financial choices.
Fear and Panic – Market downturns cause investors to sell hastily, reinforcing downward trends.
Greed and Euphoria – During bull markets, optimism leads to overvaluation and speculative bubbles.
Regret Aversion – Fear of making a wrong choice prevents investors from taking necessary risks.
---
3. Heuristics: Mental Shortcuts in Investing
Heuristics simplify decision-making but can lead to errors.
Representativeness Heuristic – Investors assume past performance predicts future results.
Herd Mentality – Following the crowd can create bubbles (e.g., the Dot-Com Bubble).
Disposition Effect – Selling winners too soon and holding losers too long due to emotional attachment.
---
4. Market Anomalies and Irrational Behavior
Behavioral finance explains several market inefficiencies.
Momentum Effect – Investors chase past performance, causing trends to persist.
Home Bias – Investors prefer domestic stocks, missing out on international diversification.
The January Effect – Stocks tend to rise in January due to psychological and tax-related reasons.
---
5. Practical Applications in Finance
Behavioral finance insights can help improve financial decision-making.
Nudging and Choice Architecture – Policies like automatic enrollment in retirement plans improve savings behavior.
Behavioral Portfolio Theory – Investors categorize assets into separate "mental accounts" rather than optimizing total portfolio risk.
Financial Advising – Understanding biases helps advisors guide clients toward rational investment strategies.
---
Conclusion
Behavioral finance highlights how psychology shapes financial decisions, leading to irrational behavior and market inefficiencies. Recognizing these biases can help investors and policymakers design strategies to mitigate their effects, improving financial outcomes.
लाइक करें 0

Blexin
Pialang
गर्म सामग्री
इंडस्ट्री
विदेशी मुद्रा कहानी Forex story
इंडस्ट्री
User Survey Questionnaire
इंडस्ट्री
User Survey Questionnaire
इंडस्ट्री
User Survey Questionnaire
इंडस्ट्री
User Survey Questionnaire
इंडस्ट्री
Participate in the survey and claim your contribution rewards!
फोरम केटेगरी

प्लेटफॉर्म

एक्सहिबिशन

एजेंट

भर्ती करना

EA

इंडस्ट्री

मार्केट

इंडेक्स
Behavioral Finance: Psychology and Decision-Making
 हाँग काँग | 2025-02-14 19:41
हाँग काँग | 2025-02-14 19:41#Firstdealofthenewyearastylz
Behavioral finance is a field that blends psychology with finance to understand how individuals and markets behave irrationally. Traditional finance assumes that investors are rational and make decisions based on all available information to maximize wealth. However, behavioral finance recognizes that psychological biases, emotions, and cognitive errors often lead to irrational financial choices.
---
Key Areas of Behavioral Finance
1. Cognitive Biases in Financial Decision-Making
Cognitive biases are systematic patterns of deviation from rationality in judgment.
Overconfidence Bias – Investors overestimate their ability to predict market movements, leading to excessive trading.
Loss Aversion – The pain of losing money is psychologically stronger than the joy of gaining it, causing risk-averse behavior.
Confirmation Bias – Investors seek information that supports their existing beliefs and ignore contradictory data.
Anchoring Bias – Decisions are influenced by irrelevant reference points, such as past stock prices.
Availability Bias – Investors give more weight to recent or easily recalled events, impacting risk perception.
---
2. Emotional Influences on Investment Behavior
Emotions play a significant role in financial choices.
Fear and Panic – Market downturns cause investors to sell hastily, reinforcing downward trends.
Greed and Euphoria – During bull markets, optimism leads to overvaluation and speculative bubbles.
Regret Aversion – Fear of making a wrong choice prevents investors from taking necessary risks.
---
3. Heuristics: Mental Shortcuts in Investing
Heuristics simplify decision-making but can lead to errors.
Representativeness Heuristic – Investors assume past performance predicts future results.
Herd Mentality – Following the crowd can create bubbles (e.g., the Dot-Com Bubble).
Disposition Effect – Selling winners too soon and holding losers too long due to emotional attachment.
---
4. Market Anomalies and Irrational Behavior
Behavioral finance explains several market inefficiencies.
Momentum Effect – Investors chase past performance, causing trends to persist.
Home Bias – Investors prefer domestic stocks, missing out on international diversification.
The January Effect – Stocks tend to rise in January due to psychological and tax-related reasons.
---
5. Practical Applications in Finance
Behavioral finance insights can help improve financial decision-making.
Nudging and Choice Architecture – Policies like automatic enrollment in retirement plans improve savings behavior.
Behavioral Portfolio Theory – Investors categorize assets into separate "mental accounts" rather than optimizing total portfolio risk.
Financial Advising – Understanding biases helps advisors guide clients toward rational investment strategies.
---
Conclusion
Behavioral finance highlights how psychology shapes financial decisions, leading to irrational behavior and market inefficiencies. Recognizing these biases can help investors and policymakers design strategies to mitigate their effects, improving financial outcomes.
लाइक करें 0
मैं भी टिप्पणियाँ करना चाहता हूँ
प्रस्तुत
0टिप्पणियाँ

अभी तक कोई टिप्पणी नहीं है। पहले एक बनाओ।
प्रस्तुत
अभी तक कोई टिप्पणी नहीं है। पहले एक बनाओ।