
2025-02-18 01:29
업계에서Understanding Interest Rate and Forex Markets
firstdealofthenewyearastylz
The relationship between interest rates and foreign exchange (forex) markets is crucial in global finance. Here's how they interact:
1. Interest Rates and Currency Value
Interest rates directly impact currency value because they influence capital flows and investor behavior.
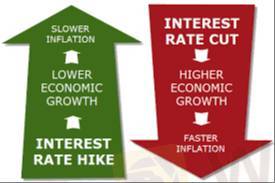
Higher Interest Rates → Stronger Currency
When a country raises interest rates, it attracts foreign investment because investors seek higher returns. This increases demand for the currency, causing appreciation.
Example: If the Federal Reserve raises U.S. interest rates, the USD strengthens as investors buy dollars to invest in U.S. assets.
Lower Interest Rates → Weaker Currency
Lower interest rates reduce the incentive for foreign investors, leading to capital outflows and depreciation of the currency.
Example: If the European Central Bank (ECB) cuts interest rates, the Euro (EUR) may weaken as investors shift to higher-yielding assets elsewhere.
2. Interest Rate Differentials and Carry Trade
Carry Trade Strategy
Traders borrow in a low-interest-rate currency and invest in a higher-interest-rate currency to profit from the rate differential.
Example: Borrowing Japanese Yen (JPY) (low rate) and investing in Australian Dollar (AUD) (higher rate).
If a central bank changes interest rates unexpectedly, it can disrupt carry trades and cause volatility.
3. Central Bank Policies and Market Reactions
Hawkish Policy (Rate Hike or Tighter Monetary Policy) → Currency Strengthens
Dovish Policy (Rate Cut or Loose Monetary Policy) → Currency Weakens
Forward Guidance (Central banks signaling future rate changes) can also move forex markets before actual rate changes.
4. Inflation, Interest Rates, and Forex
High inflation often leads to higher interest rates (to control inflation), strengthening the currency.
If inflation erodes purchasing power faster than interest rate hikes, the currency may still weaken.
5. Global Risk Sentiment & Safe-Haven Currencies
In times of economic uncertainty, investors move toward safe-haven currencies like the USD, CHF (Swiss Franc), or JPY regardless of interest rate trends.
Bottom Line
Interest rates are one of the most significant drivers of forex markets. Traders watch central banks like the Federal Reserve (Fed), ECB, Bank of Japan (BoJ), and Bank of England (BoE) closely for policy shifts.
좋아요 0

Vince024
Pialang
인기있는 콘텐츠
시장 분석
투자주체별매매 동향
시장 분석
유로존 경제 쇠퇴 위기 직면
시장 분석
국제 유가는 어디로
시장 분석
미국증시 레버리지(Leverage)·인버스(Inverse)형의 ETF, 최근 사상 최대 신
시장 분석
투기장 된 원유 ETL...첫 투자위험 발령
시장 분석
RBNZ 양적완화 확대
포럼 카테고리

플랫폼

전시회

대리상

신병 모집

EA

업계에서

시장

인덱스
Understanding Interest Rate and Forex Markets
 홍콩 | 2025-02-18 01:29
홍콩 | 2025-02-18 01:29firstdealofthenewyearastylz
The relationship between interest rates and foreign exchange (forex) markets is crucial in global finance. Here's how they interact:
1. Interest Rates and Currency Value
Interest rates directly impact currency value because they influence capital flows and investor behavior.
Higher Interest Rates → Stronger Currency
When a country raises interest rates, it attracts foreign investment because investors seek higher returns. This increases demand for the currency, causing appreciation.
Example: If the Federal Reserve raises U.S. interest rates, the USD strengthens as investors buy dollars to invest in U.S. assets.
Lower Interest Rates → Weaker Currency
Lower interest rates reduce the incentive for foreign investors, leading to capital outflows and depreciation of the currency.
Example: If the European Central Bank (ECB) cuts interest rates, the Euro (EUR) may weaken as investors shift to higher-yielding assets elsewhere.
2. Interest Rate Differentials and Carry Trade
Carry Trade Strategy
Traders borrow in a low-interest-rate currency and invest in a higher-interest-rate currency to profit from the rate differential.
Example: Borrowing Japanese Yen (JPY) (low rate) and investing in Australian Dollar (AUD) (higher rate).
If a central bank changes interest rates unexpectedly, it can disrupt carry trades and cause volatility.
3. Central Bank Policies and Market Reactions
Hawkish Policy (Rate Hike or Tighter Monetary Policy) → Currency Strengthens
Dovish Policy (Rate Cut or Loose Monetary Policy) → Currency Weakens
Forward Guidance (Central banks signaling future rate changes) can also move forex markets before actual rate changes.
4. Inflation, Interest Rates, and Forex
High inflation often leads to higher interest rates (to control inflation), strengthening the currency.
If inflation erodes purchasing power faster than interest rate hikes, the currency may still weaken.
5. Global Risk Sentiment & Safe-Haven Currencies
In times of economic uncertainty, investors move toward safe-haven currencies like the USD, CHF (Swiss Franc), or JPY regardless of interest rate trends.
Bottom Line
Interest rates are one of the most significant drivers of forex markets. Traders watch central banks like the Federal Reserve (Fed), ECB, Bank of Japan (BoJ), and Bank of England (BoE) closely for policy shifts.
좋아요 0
나 도 댓 글 달 래.
제출
0코멘트

댓글이 아직 없습니다. 첫 번째를 만드십시오.
제출
댓글이 아직 없습니다. 첫 번째를 만드십시오.