
2025-02-21 18:03
업계에서The role of the Fed in determining dollar strength
#FedRateCutAffectsDollarTrend
The Role of the Federal Reserve in Determining Dollar Strength
The Federal Reserve plays a crucial role in shaping the value of the U.S. dollar, but it is not the sole determinant. The Fed influences dollar strength primarily through monetary policy, interest rates, and market expectations, but global factors also come into play.
How the Fed Influences the Dollar
1. Interest Rate Policy & Yield Differentials
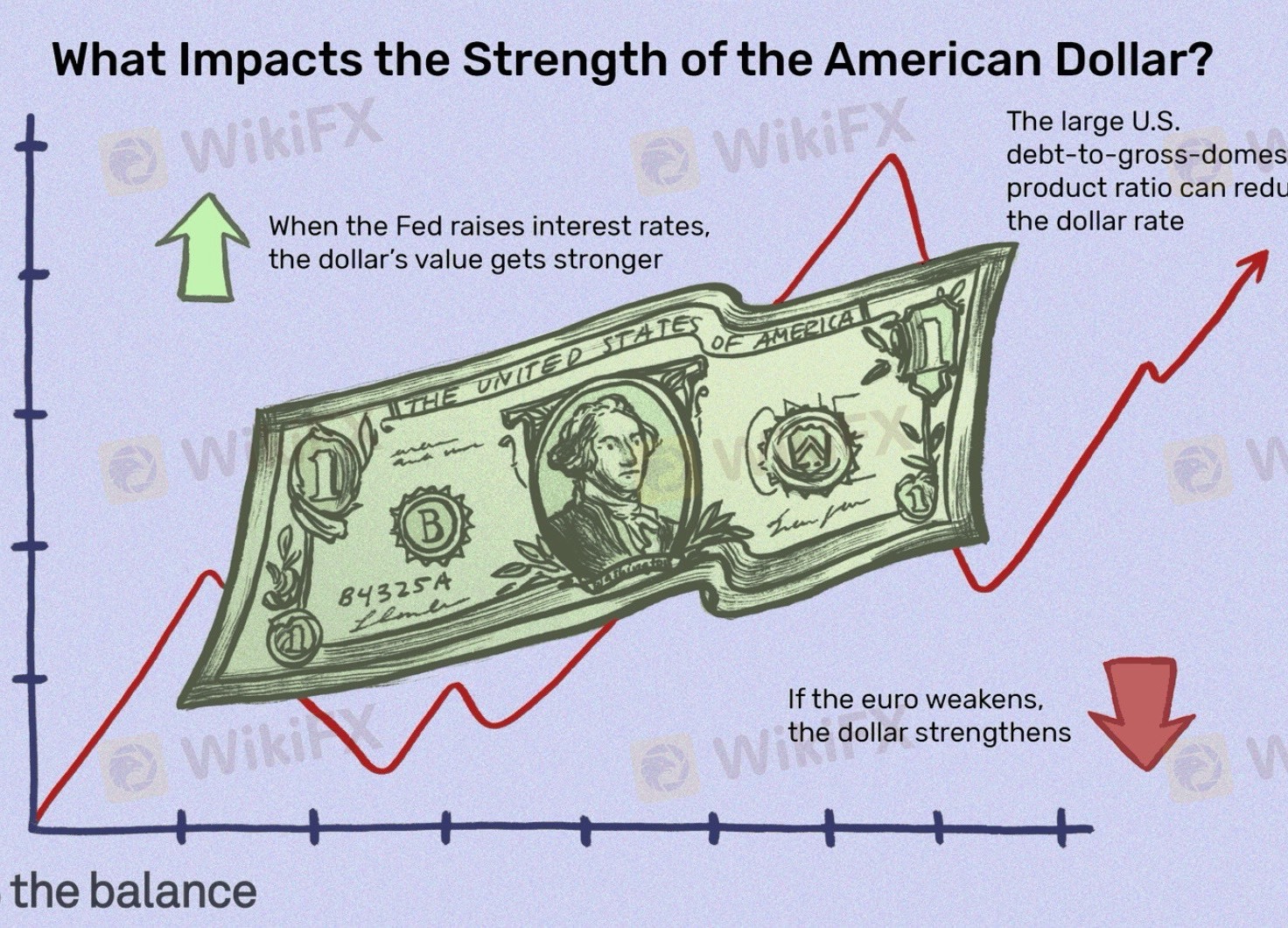
• The Fed sets the federal funds rate, which affects short-term interest rates.
• Higher rates → Stronger dollar (attracts foreign capital seeking higher returns).
• Lower rates → Weaker dollar (reduces demand for U.S. assets).
• The U.S. dollar’s strength depends on interest rate differentials—how U.S. rates compare to those in other economies.
2. Forward Guidance & Market Expectations
• The Fed signals future rate moves through speeches, dot plots, and policy statements.
• If markets expect faster rate cuts, the dollar weakens before the cuts even happen.
• If the Fed delays or slows cuts, the dollar strengthens due to higher-than-expected rates.
3. Quantitative Easing (QE) & Balance Sheet Policy
• QE (bond-buying programs) increases the money supply, typically weakening the dollar over time.
• Balance sheet tightening (QT), where the Fed reduces its holdings, can support the dollar.
• Example: 2009-2011 → The Fed’s aggressive QE weakened the dollar as liquidity surged.
4. Inflation Control & Purchasing Power
• If the Fed fights inflation aggressively with rate hikes, the dollar strengthens (e.g., 2022).
• If the Fed allows inflation to rise, the dollar’s purchasing power declines.
• Example: In the 1970s, high inflation weakened the dollar until the Fed raised rates sharply in the early 1980s.
Limits to the Fed’s Control Over the Dollar
1. Global Economic Conditions
• If global markets are unstable (e.g., financial crises), demand for the dollar can increase as a safe haven, even if the Fed is cutting rates.
• Example: In early 2020 (COVID crisis), the dollar surged despite emergency rate cuts.
2. Other Central Banks’ Policies
• If the ECB, BoJ, or others are also easing, the dollar may stay strong despite Fed rate cuts.
• Example: In **
좋아요 0
FX2192840773
거래자
인기있는 콘텐츠
시장 분석
투자주체별매매 동향
시장 분석
유로존 경제 쇠퇴 위기 직면
시장 분석
국제 유가는 어디로
시장 분석
미국증시 레버리지(Leverage)·인버스(Inverse)형의 ETF, 최근 사상 최대 신
시장 분석
투기장 된 원유 ETL...첫 투자위험 발령
시장 분석
RBNZ 양적완화 확대
포럼 카테고리

플랫폼

전시회

대리상

신병 모집

EA

업계에서

시장

인덱스
The role of the Fed in determining dollar strength
 인도 | 2025-02-21 18:03
인도 | 2025-02-21 18:03#FedRateCutAffectsDollarTrend
The Role of the Federal Reserve in Determining Dollar Strength
The Federal Reserve plays a crucial role in shaping the value of the U.S. dollar, but it is not the sole determinant. The Fed influences dollar strength primarily through monetary policy, interest rates, and market expectations, but global factors also come into play.
How the Fed Influences the Dollar
1. Interest Rate Policy & Yield Differentials
• The Fed sets the federal funds rate, which affects short-term interest rates.
• Higher rates → Stronger dollar (attracts foreign capital seeking higher returns).
• Lower rates → Weaker dollar (reduces demand for U.S. assets).
• The U.S. dollar’s strength depends on interest rate differentials—how U.S. rates compare to those in other economies.
2. Forward Guidance & Market Expectations
• The Fed signals future rate moves through speeches, dot plots, and policy statements.
• If markets expect faster rate cuts, the dollar weakens before the cuts even happen.
• If the Fed delays or slows cuts, the dollar strengthens due to higher-than-expected rates.
3. Quantitative Easing (QE) & Balance Sheet Policy
• QE (bond-buying programs) increases the money supply, typically weakening the dollar over time.
• Balance sheet tightening (QT), where the Fed reduces its holdings, can support the dollar.
• Example: 2009-2011 → The Fed’s aggressive QE weakened the dollar as liquidity surged.
4. Inflation Control & Purchasing Power
• If the Fed fights inflation aggressively with rate hikes, the dollar strengthens (e.g., 2022).
• If the Fed allows inflation to rise, the dollar’s purchasing power declines.
• Example: In the 1970s, high inflation weakened the dollar until the Fed raised rates sharply in the early 1980s.
Limits to the Fed’s Control Over the Dollar
1. Global Economic Conditions
• If global markets are unstable (e.g., financial crises), demand for the dollar can increase as a safe haven, even if the Fed is cutting rates.
• Example: In early 2020 (COVID crisis), the dollar surged despite emergency rate cuts.
2. Other Central Banks’ Policies
• If the ECB, BoJ, or others are also easing, the dollar may stay strong despite Fed rate cuts.
• Example: In **
좋아요 0
나 도 댓 글 달 래.
제출
0코멘트

댓글이 아직 없습니다. 첫 번째를 만드십시오.
제출
댓글이 아직 없습니다. 첫 번째를 만드십시오.