
2025-02-06 09:34
IndustriMacroeconomics theory
#firstdealofthenewyearastylz
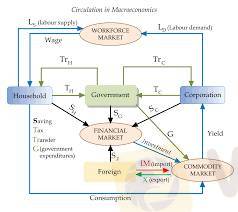
Macroeconomics is a branch of economics that studies the behavior and performance of an economy as a whole. It focuses on aggregate changes and the overall functioning of the economy, rather than individual markets. Here are the key components and theories of macroeconomics:
1. Aggregate Demand and Supply: Macroeconomics analyzes the total demand (aggregate demand) and total supply (aggregate supply) in an economy. Aggregate demand is the total quantity of goods and services demanded across all levels of the economy at a given overall price level, while aggregate supply is the total production of goods and services at a given price level.
2. National Income Accounting: This involves measuring a country's economic performance through indicators like Gross Domestic Product (GDP), Gross National Product (GNP), and Net National Product (NNP). GDP measures the total value of all goods and services produced over a specific time period within a country.
3. Business Cycles: Macroeconomics studies the fluctuations in economic activity over time, known as business cycles. These cycles consist of periods of expansion (growth) and contraction (recession) and are influenced by various factors including consumer confidence, investment, and government policies.
4. Monetary Policy: This refers to the actions taken by a country's central bank to control the money supply and interest rates to achieve macroeconomic objectives such as controlling inflation, consumption, growth, and liquidity. Tools include open market operations, discount rates, and reserve requirements.
5. Fiscal Policy: This involves government spending and taxation policies to influence economic conditions. By adjusting spending levels and tax rates, governments can impact overall economic activity, aggregate demand, and employment levels.
6. Inflation and Unemployment: Macroeconomics examines the relationship between inflation (the rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services rises) and unemployment (the percentage of the labor force that is jobless). The Phillips Curve illustrates this trade-off, suggesting that lower unemployment can lead to higher inflation.
7. Economic Growth: This aspect focuses on the long-term increase in a country's productive capacity, often measured by GDP growth. Factors that contribute to economic growth include technological advancements, capital accumulation, and improvements in labor productivity.
8. International Economics: Macroeconomics also considers how economies interact on a global scale, including trade balances, exchange rates, and the impact of international policies on domestic economies.
Overall, macroeconomic theory provides a framework for understanding how economies operate and how various factors influence economic performance. It helps policymakers design strategies to promote economic stability and growth.
My AI currently does not provide accurate information for events that occurred after December 2023. Please check other reliable sources for more up-to-date information.
Suka 0

Monix
Pialang
Diskusi populer
Industri
СЕКРЕТ ЖЕНСКОГО ФОРЕКСА
Industri
УКРАИНА СОБИРАЕТСЯ СТАТЬ ЛИДЕРОМ НА РЫНКЕ NFT
Industri
Alasan Investasi Bodong Tumbuh Subur di Indonesia
Industri
Forex Eropa EURUSD 29 Maret: Berusaha Naik dari Terendah 4 Bulan
Analisis pasar
Bursa Asia Kebakaran, Eh... IHSG Ikut-ikutan
Analisis pasar
Kinerja BUMN Karya Disinggung Dahlan Iskan, Sahamnya Pada Rontok
Klasifikasi pasar

Platform

Pameran

Agen

Perekrutan

EA

Industri

Pasar

Indeks
Macroeconomics theory
 Hong Kong | 2025-02-06 09:34
Hong Kong | 2025-02-06 09:34#firstdealofthenewyearastylz
Macroeconomics is a branch of economics that studies the behavior and performance of an economy as a whole. It focuses on aggregate changes and the overall functioning of the economy, rather than individual markets. Here are the key components and theories of macroeconomics:
1. Aggregate Demand and Supply: Macroeconomics analyzes the total demand (aggregate demand) and total supply (aggregate supply) in an economy. Aggregate demand is the total quantity of goods and services demanded across all levels of the economy at a given overall price level, while aggregate supply is the total production of goods and services at a given price level.
2. National Income Accounting: This involves measuring a country's economic performance through indicators like Gross Domestic Product (GDP), Gross National Product (GNP), and Net National Product (NNP). GDP measures the total value of all goods and services produced over a specific time period within a country.
3. Business Cycles: Macroeconomics studies the fluctuations in economic activity over time, known as business cycles. These cycles consist of periods of expansion (growth) and contraction (recession) and are influenced by various factors including consumer confidence, investment, and government policies.
4. Monetary Policy: This refers to the actions taken by a country's central bank to control the money supply and interest rates to achieve macroeconomic objectives such as controlling inflation, consumption, growth, and liquidity. Tools include open market operations, discount rates, and reserve requirements.
5. Fiscal Policy: This involves government spending and taxation policies to influence economic conditions. By adjusting spending levels and tax rates, governments can impact overall economic activity, aggregate demand, and employment levels.
6. Inflation and Unemployment: Macroeconomics examines the relationship between inflation (the rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services rises) and unemployment (the percentage of the labor force that is jobless). The Phillips Curve illustrates this trade-off, suggesting that lower unemployment can lead to higher inflation.
7. Economic Growth: This aspect focuses on the long-term increase in a country's productive capacity, often measured by GDP growth. Factors that contribute to economic growth include technological advancements, capital accumulation, and improvements in labor productivity.
8. International Economics: Macroeconomics also considers how economies interact on a global scale, including trade balances, exchange rates, and the impact of international policies on domestic economies.
Overall, macroeconomic theory provides a framework for understanding how economies operate and how various factors influence economic performance. It helps policymakers design strategies to promote economic stability and growth.
My AI currently does not provide accurate information for events that occurred after December 2023. Please check other reliable sources for more up-to-date information.
Suka 0
Saya juga ingin komentar
Tanyakan pertanyaan
0Komentar

Belum ada yang berkomentar, segera jadi yang pertama
Tanyakan pertanyaan
Belum ada yang berkomentar, segera jadi yang pertama