
2025-02-21 18:03
IndustriThe role of the Fed in determining dollar strength
#FedRateCutAffectsDollarTrend
The Role of the Federal Reserve in Determining Dollar Strength
The Federal Reserve plays a crucial role in shaping the value of the U.S. dollar, but it is not the sole determinant. The Fed influences dollar strength primarily through monetary policy, interest rates, and market expectations, but global factors also come into play.
How the Fed Influences the Dollar
1. Interest Rate Policy & Yield Differentials
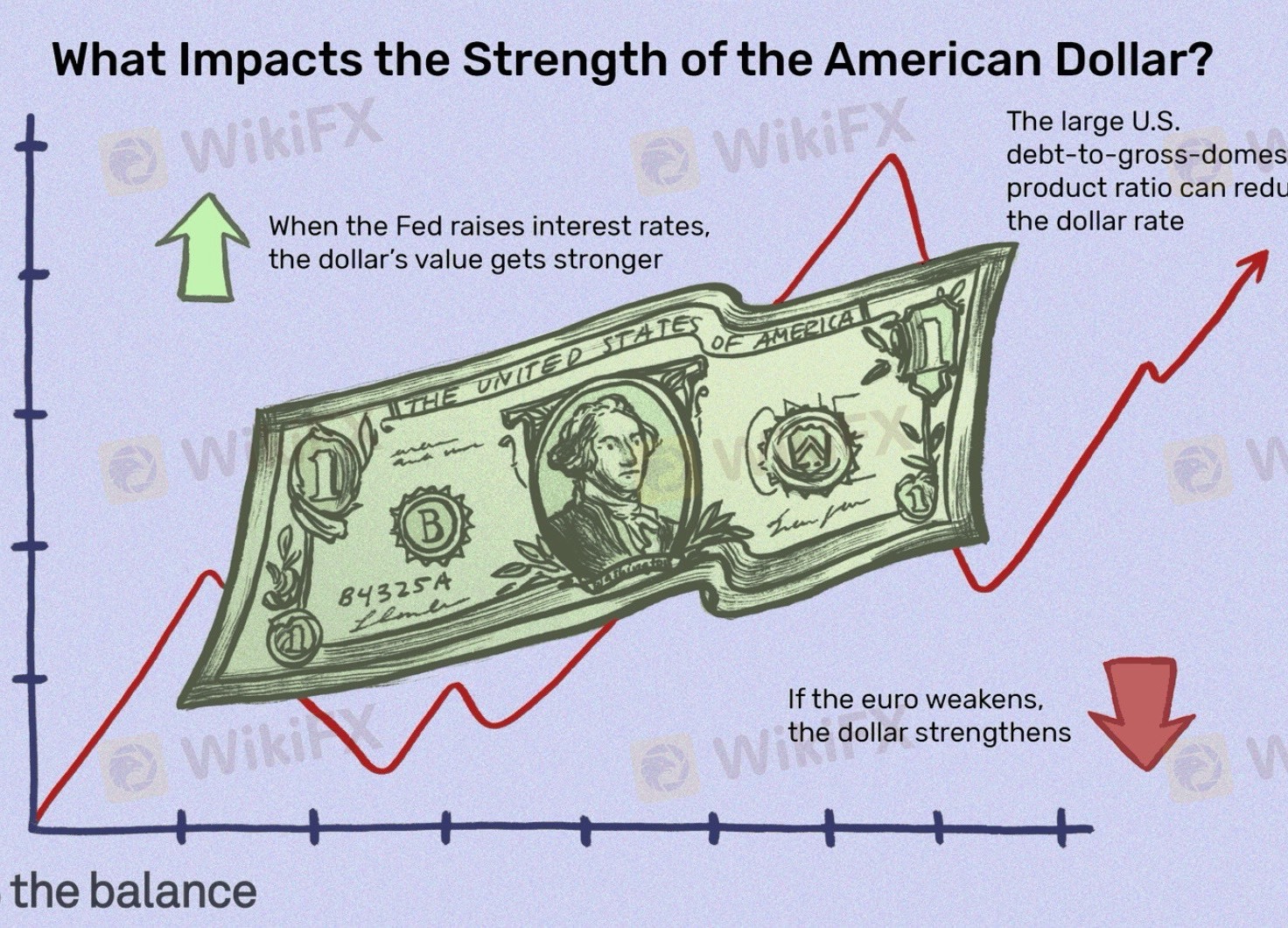
• The Fed sets the federal funds rate, which affects short-term interest rates.
• Higher rates → Stronger dollar (attracts foreign capital seeking higher returns).
• Lower rates → Weaker dollar (reduces demand for U.S. assets).
• The U.S. dollar’s strength depends on interest rate differentials—how U.S. rates compare to those in other economies.
2. Forward Guidance & Market Expectations
• The Fed signals future rate moves through speeches, dot plots, and policy statements.
• If markets expect faster rate cuts, the dollar weakens before the cuts even happen.
• If the Fed delays or slows cuts, the dollar strengthens due to higher-than-expected rates.
3. Quantitative Easing (QE) & Balance Sheet Policy
• QE (bond-buying programs) increases the money supply, typically weakening the dollar over time.
• Balance sheet tightening (QT), where the Fed reduces its holdings, can support the dollar.
• Example: 2009-2011 → The Fed’s aggressive QE weakened the dollar as liquidity surged.
4. Inflation Control & Purchasing Power
• If the Fed fights inflation aggressively with rate hikes, the dollar strengthens (e.g., 2022).
• If the Fed allows inflation to rise, the dollar’s purchasing power declines.
• Example: In the 1970s, high inflation weakened the dollar until the Fed raised rates sharply in the early 1980s.
Limits to the Fed’s Control Over the Dollar
1. Global Economic Conditions
• If global markets are unstable (e.g., financial crises), demand for the dollar can increase as a safe haven, even if the Fed is cutting rates.
• Example: In early 2020 (COVID crisis), the dollar surged despite emergency rate cuts.
2. Other Central Banks’ Policies
• If the ECB, BoJ, or others are also easing, the dollar may stay strong despite Fed rate cuts.
• Example: In **
Suka 0
FX2192840773
Трейдер
Diskusi populer
Industri
СЕКРЕТ ЖЕНСКОГО ФОРЕКСА
Industri
УКРАИНА СОБИРАЕТСЯ СТАТЬ ЛИДЕРОМ НА РЫНКЕ NFT
Industri
Alasan Investasi Bodong Tumbuh Subur di Indonesia
Industri
Forex Eropa EURUSD 29 Maret: Berusaha Naik dari Terendah 4 Bulan
Analisis pasar
Bursa Asia Kebakaran, Eh... IHSG Ikut-ikutan
Analisis pasar
Kinerja BUMN Karya Disinggung Dahlan Iskan, Sahamnya Pada Rontok
Klasifikasi pasar

Platform

Pameran

Agen

Perekrutan

EA

Industri

Pasar

Indeks
The role of the Fed in determining dollar strength
 India | 2025-02-21 18:03
India | 2025-02-21 18:03#FedRateCutAffectsDollarTrend
The Role of the Federal Reserve in Determining Dollar Strength
The Federal Reserve plays a crucial role in shaping the value of the U.S. dollar, but it is not the sole determinant. The Fed influences dollar strength primarily through monetary policy, interest rates, and market expectations, but global factors also come into play.
How the Fed Influences the Dollar
1. Interest Rate Policy & Yield Differentials
• The Fed sets the federal funds rate, which affects short-term interest rates.
• Higher rates → Stronger dollar (attracts foreign capital seeking higher returns).
• Lower rates → Weaker dollar (reduces demand for U.S. assets).
• The U.S. dollar’s strength depends on interest rate differentials—how U.S. rates compare to those in other economies.
2. Forward Guidance & Market Expectations
• The Fed signals future rate moves through speeches, dot plots, and policy statements.
• If markets expect faster rate cuts, the dollar weakens before the cuts even happen.
• If the Fed delays or slows cuts, the dollar strengthens due to higher-than-expected rates.
3. Quantitative Easing (QE) & Balance Sheet Policy
• QE (bond-buying programs) increases the money supply, typically weakening the dollar over time.
• Balance sheet tightening (QT), where the Fed reduces its holdings, can support the dollar.
• Example: 2009-2011 → The Fed’s aggressive QE weakened the dollar as liquidity surged.
4. Inflation Control & Purchasing Power
• If the Fed fights inflation aggressively with rate hikes, the dollar strengthens (e.g., 2022).
• If the Fed allows inflation to rise, the dollar’s purchasing power declines.
• Example: In the 1970s, high inflation weakened the dollar until the Fed raised rates sharply in the early 1980s.
Limits to the Fed’s Control Over the Dollar
1. Global Economic Conditions
• If global markets are unstable (e.g., financial crises), demand for the dollar can increase as a safe haven, even if the Fed is cutting rates.
• Example: In early 2020 (COVID crisis), the dollar surged despite emergency rate cuts.
2. Other Central Banks’ Policies
• If the ECB, BoJ, or others are also easing, the dollar may stay strong despite Fed rate cuts.
• Example: In **
Suka 0
Saya juga ingin komentar
Tanyakan pertanyaan
0Komentar

Belum ada yang berkomentar, segera jadi yang pertama
Tanyakan pertanyaan
Belum ada yang berkomentar, segera jadi yang pertama