Quantitative Easing (QE) Explained: Central Bank Tool for Growth
Abstract:What is quantitative easing (QE) and how do central banks like the Fed and ECB use it? Learn how QE supplements monetary policy when rate cuts dont cut it.
Quantitative Easing Explained: Main Talking Points
定量宽松解释:主要讨论要点
With interest rates near zero, the Federal Reserve ventured another policy tool in quantitative easing
利率接近于零,美联储冒险量化宽松政策的另一个政策工具
After years of QE, the Bank of Japan has experienced diminishing economic and financial returns
经过多年的量化宽松政策,日本银行的经济和财务回报日益减少
Similarly, the ECB has engaged in long-term refinancing operations (LTROs) as a form of quantitative easing, but their effectiveness remains in question
同样,欧洲央行已将长期再融资操作(LTRO)作为一种量化宽松政策,但其有效性仍然存在问题
{4}
How Does Quantitative Easing Work?
{4}
Quantitative easing (referred to as ‘QE’) is a monetary policy tool typically used by central banks to stimulate their domestic economy when more traditional methods are spent. The central bank buys securities – most frequently government bonds – from its member banks, effectively increasing the supply of money in the economy.
量化宽松(简称'QE')是一个当采用更传统的方法时,中央银行通常使用货币政策工具来刺激国内经济。中央银行从其成员银行购买证券 - 最常见的是政府债券 - 有效地增加了经济中的货币供应量。
With increased supply, the cost of money is reduced which makes it cheaper for businesses to borrow money to use for expansion. This has a similar effect to the standard interest short-term interest rate cuts that central banks employ; but depending on what they purchase, such efforts can lower the cost for significantly longer loans. That could more directly influence lending for homes, autos and small businesses.
随着供应增加,资金成本降低,使企业借钱用于扩张更便宜。这与中央银行采用的标准利率短期利率削减效果相似;但取决于他们购买的产品,此类努力可以降低长期贷款的成本。这可能更直接地影响房屋,汽车和小企业的贷款。
The Federal Reserve Bank (FED) Quantitative Easing Policy
联邦储备银行(FED)量化宽松政策
As the central bank of the United States, the Federal Reserve has a duty to provide the nation with a safer, flexible and more stable monetary and financial system. That is often boiled down into a stated dual mandate of steady inflation and low unemployment. In pursuit of these objectives, the Fed is allotted a series of monetary policy tools that allow it to influence the US Dollar and the money supply in the country. While raising and lowering the Federal Funds rate is the most widely known tool, the central banks balance sheet has become one of heightened importance and investor interest.
作为美国的中央银行,美联储有责任为国家提供更安全,更灵活,更稳定的货币和金融体系。这通常归结为稳定通胀和低失业率的双重要求。为了实现这些目标,美联储分配了一系列货币政策工具,使其能够影响美元和该国的货币供应。虽然提高和降低联邦基金利率是最广为人知的工具,但中央银行的资产负债表已成为高度重要和投资者兴趣之一。
Federal Reserve Bank Total Assets
美联储巴k总资产
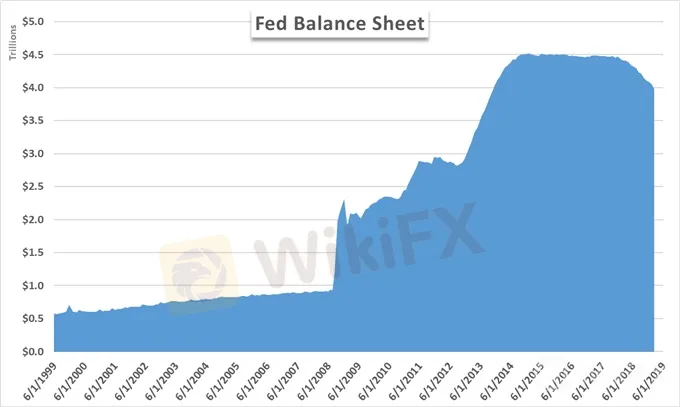
Source: FRED
来源:FRED
Simply put, the Fed‘s balance sheet is the same as any other balance sheet. In the Fed’s case, it records the collection of distinct assets and liabilities across all the Federal Reserve bank branches. The bank can use these assets and liabilities as an unconventional or supplementary monetary policy tool, particularly when interest rates are already low and confer limited potential with further policy efforts.
简而言之,美联储的资产负债表与任何其他资产负债表相同。在美联储的案例中,它记录了所有联邦储备银行分行的不同资产和负债的收集情况。银行可以将这些资产和负债用作非常规或补充货币政策工具,特别是当利率已经很低并且通过进一步的政策努力赋予有限的潜力时。
In 2008, as the United States economy entered a recession amid the Great Financial Crisis, the Federal Reserve announced a series of interest rate cuts. As a typical expansionary tool, the cuts were intended to spur spending thereby improving the economy. However, even with interest rates near zero, economic recovery failed to take hold.
2008年,美国经济在大金融危机中陷入衰退,美联储宣布了一系列降息措施。作为一种典型的扩张工具,减产旨在刺激消费,从而改善经济。然而,即使利率接近于零,经济复苏也未能成功。
Then, in November 2008, the Federal Reserve announced its initial round of Quantitative Easing, popularly known as QE1. The announcement saw the Fed massively shift its standard market operations as it began to purchase significant amounts of treasury bills, notes and bonds, along with asset- and mortgage-backed securities of high quality. The purchases effectively increased the supply of money in the US economy and made access to capital less expensive. The buying program lasted from December 2008 to March 2010 and was accompanied by another cut to the Fed Funds rate, resulting in a new range of 0 to 0.25% interest.
然后,在2008年11月,美联储宣布其首轮定量宽松,俗称QE1 。该公告显示,美联储开始大量转移其标准市场业务,因为它开始购买大量国库券,票据和债券,以及高质量的资产和抵押贷款支持证券。这些购买有效地增加了美国经济中的货币供应,使得获得资本的成本更低。购买计划从2008年12月持续到2010年3月,并伴随着美联储基金利率的再次下调,导致新的0至0.25%的利息范围。
Change in Fed Balance Sheet due to Quantitative Easing
美联储的变化由于量化宽松而产生的资产负债表

Source: Bloomberg
来源:Bloomberg
With the Federal Funds rate near 0, and not willing to explore negative rates at the time, the central bank had effectively expended all its expansionary monetary policy tools. Thus, quantitative easing became an important part of the central banks toolbox to boost economic growth and right the capsized ship that was the US economy.
联邦基金利率接近0,不愿意当时xplore的负利率,央行已经有效地扩展了其所有扩张性货币政策工具。因此,量化宽松政策成为中央银行工具箱的一个重要组成部分,以促进经济增长,并使美国经济的倾覆船舶正确化。
To further aid recovery, the Fed pursued subsequent rounds of Quantitative Easing, now known as QE2 from November 2010 to June 2011 and QE3 from September 2012 to December 2013. The purchase programs targeted similar assets and helped to prop up perceived growth – as well as capital markets as a side effect – in the US until the central bank finally reversed course by raising its benchmark rate for the first time in December 2015.
为了进一步帮助经济复苏,美联储随后追求定量宽松的轮次,现在称为2010年11月至2011年6月的QE2和2012年9月至2013年12月的QE3。购买计划针对类似的资产,并有助于支持增长 - 以及资本市场的副作用 - 美国直到央行最终通过在2015年12月首次提高基准利率来扭转局面。
Having already started to reduce its balance sheet in 2018, we have seen debate over a sustained Quantitative Tightening (reducing the balance sheet) pop up in 2019. Many Federal Reserve officials have supported the slow drawdown of the banks balance sheet and advocated for further normalization as the US economy boasts over a decade of economic expansion. However, uneven growth and external risks like trade wars have complicated the issue of this exceptional support.
我们已经开始在2018年减少其资产负债表,我们在2019年出现了关于持续量化紧缩(减少资产负债表)的争论。许多美联储官员都有支持银行资产负债表缓慢缩减,并进一步提倡正常化,因为美国经济已经经历了十多年的经济扩张。然而,不平衡的增长和贸易战等外部风险使这种特殊支持的问题变得复杂。
The Bank of Japan (BOJ) Quantitative Easing Policy
日本央行(BOJ)量化宽松政策
Japans central bank is another financial institution that has employed the use of quantitative easing, but with varying degrees of success. One of the first instances occurred between October 1997 and October 1998 when the BOJ purchased trillions in Yen of commercial paper in an attempt to help banks through a period of low growth, low interest rates and trouble from bad bank loans. However, growth remained subdued.
日本央行是另一家采用量化宽松政策的金融机构,但取得了不同程度的成功。其中一个例子发生在1997年10月到1998年10月之间,当时日本央行以日元购买数万亿商业票据,试图帮助银行度过低增长,低利率和不良银行贷款的困境。然而,增长仍然低迷。
In light of the underwhelming impact, the Bank of Japan increased asset purchases between March 2001 and December 2004. This round of purchases targeted long-term government bonds and injected 35.5 trillion Yen in liquidity to Japanese banks. While the purchases were moderately effective, the purchase of long-term government bonds suppressed asset yields and at the advent of the Great Financial Crisis, Japans growth vanished once again. Since then, the Bank of Japan has conducted numerous rounds of QE and qualitative monetary easing (QQE) all of which were largely ineffective as the country struggles with low economic growth despite a negative interest rate environment.
鉴于影响不大的影响,日本银行在2001年3月至2004年12月期间增加了资产购买量购买有针对性的长期政府债券,向日本银行注入35.5万亿日元的流动资金。虽然购买效果适度,但购买长期政府债券会抑制资产收益率,而在金融危机爆发后,日本经济增长再次消失。从那以后,日本央行进行了多轮量化宽松和定性货币宽松政策(QQE),尽管利率环境为负,但由于该国经济增长率较低,所以这些都基本无效。
{26}

Source: Bloomberg
{26}
Today, the Bank of Japan has branched out to other forms of asset purchases with varying degrees of quality. Alongside previous purchases of commercial paper, the bank has built up considerable ownership of the countrys exchange traded fund (ETF) market and Japanese real estate investment trusts or J-REITs.
今天,日本银行已开始以不同程度的质量购买其他形式的资产。除了之前购买商业票据外,该银行已经建立了对该国交易所交易基金(ETF)市场和日本房地产投资信托基金或J-REIT的大量所有权。

Source: Bloomberg
资料来源:Bloomberg
The BOJ began ETF purchases in 2010 and as of 2Q 2018 owned roughly 70% of the total Japanese ETF market. Further, these broad purchases have made the central bank a majority shareholder in over 40% of all public Japanese corporations according to Bloomberg. Thus, the quality and credit rating of these holdings by the central bank are fundamentally weaker than that of a government issued assets like Japanese Government Bonds (JGBs) and differ considerably from holdings of the Federal Reserve.
日本央行于2010年开始购买ETF,截至2018年第二季度,日本交易所ETF市场约占70%。此外,据彭博社报道,这些广泛的购买使得中央银行成为所有日本公共公司40%以上的大股东。因此,中央银行持有的这些资产的质量和信用评级基本上弱于日本政府债券(JGBs)等政府发行资产的质量和信用评级,并且与美联储持有的资产相差很大。
{30}
The Bank of England (BOE) Quantitative Easing Policy
{30}
Like the previously mentioned central banks, the BOE has amassed large sums of local government bonds (GILTs) and corporate bonds through its own quantitative easing. The policy was pursued to bolster the UKs economy during the height of the global recession which would eventually carry over to the added risk of political risks from a Scottish Referendum vote, General Election and eventually the Brexit. At the same time, the bank has increased its overnight lending rate slowly.
与前面提到的央行一样,京东方已积累了大量地方政府债券(GILTs)和语料库e通过自己的量化宽松债券。在全球经济衰退的高峰时期,该政策旨在加强英国经济,这最终将导致苏格兰公投,大选和最终英国退欧的政治风险增加。与此同时,银行缓慢增加隔夜贷款利率。

Source: Bloomberg
来源:Bloomberg
{33}
In contrast to its American and Japanese counterparts, the overall holdings of the UK‘s central bank are significantly smaller. When compared to national GDP, the Bank of England’s holdings amount to a mere 5.7% in early 2019, paling in comparison to Japans holdings that equate to more than 100% of GDP. The relatively small holdings may allow the bank to act more effectively in the future as the diminishing returns of QE have yet to take hold.
{33}

Source: Bloomberg
资料来源:Bloomberg
At present, the efficacy of the BOEs quantitative easing strategy appears to top that of the BOJ and fall inline with that of the Federal Reserve. As the uncertainties of Brexit persist, the bank may decide to maintain its safety net or perhaps even further its monetary policy measures. That being said, the bank would remain far less committed to quantitative easing than its neighbor, the European Central Bank.
目前,英国央行量化宽松策略的效率似乎高于日本央行,并且与美联储一致。由于英国退欧的不确定性持续存在,银行可能会决定维持其安全网或甚至可能进一步采取货币政策措施。话虽这么说,该银行仍然会比其邻国欧洲中央银行更少致力于量化宽松政策。
The European Central Bank (ECB) Quantitative Easing Policy
欧洲央行(ECB)量化宽松政策
The ECB is another major central bank that has pursued quantitative easing as an expansionary tool – though its foray into the now conventional QE came significantly latter than the Feds. In its most recent round of easing, the European Central Bank spent nearly $3 trillion buying government bonds and corporate debt, along with asset-backed securities and covered bonds.
欧洲央行是另一家主要的中央银行,作为前者采取量化宽松政策回转工具 - 虽然它进入现在的传统量化宽松政策的时间明显晚于联邦调查局。在最近的一轮宽松政策中,欧洲中央银行花了将近3万亿美元购买政府债券和公司债券,以及资产支持证券和担保债券。
The purchases were conducted from March 2015 to December 2018 in an effort to avoid sub-zero inflation from plaguing the European bloc which was still in recovery from the dual scourge of the global recession and then the Eurozone Debt Crisis. According to Reuters, the purchases came at a pace of 1.3 million Euros a minute, equating to 7,600 Euros per person in the bloc.
进行购买从2015年3月到2018年12月,努力避免零度通货膨胀困扰欧洲集团,欧洲集团仍在从全球经济衰退和欧元区债务危机的双重祸害中复苏。据路透社报道,购买的速度为每分钟130万欧元,相当于集团每人7,600欧元。

Source: Bloomberg
资料来源:Bloomberg
Like Japan, the ECBs easing rounds proved rather ineffective. In early 2019, the bank announced another round of easing through targeted long-term refinancing operations or TLTROs, just months after the end of its opened-ended QE program and as interest rates remain at 0. TLTROs provide an injection of low interest rate funding to banks in the Eurozone in an effort to provide greater bank liquidity and lower sovereign debt yields. The loans carry a maturity of one to four years.
与日本一样,欧洲央行的宽松政策证明相当无效。在2019年初,该银行通过有针对性的长期再融资操作或TLTRO宣布了另一轮宽松政策,仅在其开放式QE计划结束几个月后,利率维持在0. TLTRO提供低利率资金注入向欧元区银行提供更多银行流动性和降低主权债务收益率。贷款的期限为一至四年。

Source: Bloomberg
来源:Bloomberg
TLTROs aim to stabilize the balance sheet of private banks and their liquidity ratio. A stronger liquidity ratio allows the bank to lend more readily which in-turn, pushes down interest rates and should allow for inflation. However, years of monetary stimulus can see diminishing returns and have negative implications.
TLTRO旨在稳定私人银行的资产负债表及其流动资金比率。流动性比率越高,银行就越容易放贷,从而降低利率,并应允许通货膨胀。然而,多年的货币刺激措施可以看到收益递减并产生负面影响。
Negative Effects of QE: Balance Sheet Use and Diminishing Returns
量化宽松的负面影响:资产负债表的使用和减少回报
While QE proved fruitful for the Federal Reserve and the United States, the monetary policy tool has proved less effective for the central banks of Japan and Europe and has even contributed some negative consequences. For the Japanese economy, years of expansionary policy has resulted in deflation and the banks balance sheet now carries more value than the GDP of the country.
虽然量化宽松政策证明对美联储和美国富有成效,但货币政策工具对日本和欧洲中央银行来说效果较差,甚至造成了一些负面后果。对于日本经济而言,多年的扩张性政策导致了通货紧缩,银行资产负债表现在的价值超过了国内生产总值。
Further, its large share of ownership of the ETF, JRIET and government bond market may put it at heightened risk in the eventuality of an economic downturn. Despite numerous rounds of stimulus and negative interest rates, economic growth has failed to take hold and the Japanese central bank is wading into unknown monetary policy territory.
此外,它的所有权份额很大。 ETF,JRIET和政府债券市场可能会在经济衰退的可能性中将其置于高风险之中。尽管出现了多轮刺激和负利率,但经济增长未能实现,日本央行正在涉足未知的货币政策领域。
Similarly, the ECB has seen its own form of quantitative easing exert less influence over the European economy as inflation and growth remain muted in the bloc.
同样,欧洲央行也看到了自由形式的量化宽松政策对欧洲经济影响较小,因为整个集团的通胀和增长依然低迷。
The Impact of Quantitative Easing on Currencies
量化宽松对货币的影响
{49}
Fundamentally, the use of quantitative easing increases the supply of a currency. According to the commanding principles of supply and demand, such a change should result in the price of that currency decreasing. However, as currencies are traded in pairs, the resulting weakness in one currency is relative to its counterpart.
{49}
With the current monetary policy climate trending toward flush supply and dovish tones, few currencies herald absolute strength. That said, strength has recently been garnered through an almost best-of-the-rest mentality in which a dovish shift from one central bank is followed shortly thereafter with dovishness from another bank. Such subtle competitive policies can turn more aggressive, resulting in what is termed a ‘currency war’.
随着当前货币政策气候趋向于冲洗供应和温和的基调,几乎没有货币先驱绝对的力量。也就是说,最近通过几乎最好的休息心态获得了力量,其中不久之后,一家中央银行的温和转变伴随着来自另一家银行的鸽派。这种微妙的竞争政策可能变得更加激进,导致所谓的“货币战争”。

Source: Bloomberg
来源:Bloomberg
Consequently, the global supply of money has ballooned while the relative value of currencies remains in flux. In the current monetary policy climate, differences in approach have largely become a comparison in dovishness. Among the major central banks, few stand on the hawkish side of policy and fewer still have plans to raise their central interest rate. Instead, officials have resorted to rounds of capital injection as quantitative easing appears to be gaining popularity as a monetary policy tool – though whether it remains as a permanent one remains to be seen.
因此全球货币供应量激增,而货币的相对价值仍在不断变化。在当前的货币政策环境中,方法上的差异在很大程度上已成为温和的比较。在主要的中央银行中,很少有人站在政策的鹰派一边,更少的人仍有提高中央利率的计划。相反,由于量化宽松政策作为一种货币政策工具似乎越来越受欢迎,官员已经采取了多轮资本注入 - 尽管它是否仍然是永久性的,仍有待观察。
Read more

Fed's Dovish Surprise: Will PCE Amplify Further Next Week?
In January, the U.S durable goods orders have fell 6.1% vs -4.5% expected, marking the largest decrease in nearly four years, while business investment in equipment appeared to have eased, indicating a decrease in economic momentum at the beginning of the year.The UK's Gross Domestic Product (GDP) experienced a contraction of -0.3% in Q4, worse than the expected decline of -0.1%. This downturn was attributed to declines across all primary sectors and caused the UK to enter a technical recession.

Crude Oil Prices at Risk if US Economic Data Cool Fed Rate Cut Bets
Crude oil prices may fall if upbeat US retail sales and consumer confidence data cool Fed rate cut bets and sour risk appetite across financial markets.

EURUSD Fails to Test 2019 Low, RSI Flashes Bullish Signal After ECB
EURUSD fails to test the 2019-low (1.0926) following the ECB meeting, with the Relative Strength Index (RSI) breaking out of the bearish formation carried over from June.

Gold, Crude Oil Prices at Risk if ECB, US CPI Cool Stimulus Hopes
Gold and crude oil prices may be pressured if the ECB underwhelms investors dovish hopes while higher US core inflation cools Fed rate cut expectations.
WikiFX Broker
Latest News
Consumer Credit Smashes All Estimates As Monthly Credit Card Debt Unexpectedly Surges By Most In 2 Years
CAD Outlook: Historic Drop in Student Enrollment Signals Demographic Drag
South African Rand (ZAR) on Alert: DA Leadership Uncertainty Rattles Markets
Gold's Historic Volatility: Liquidation Crash Meets Geopolitical Deadlock
Treasury Yields Surge as Refunding Expectations Dash; Warsh 'Hawk' Factor Looms
ZarVista Legitimacy Check: Addressing Fears: Is This a Fake Broker or a Legitimate Trading Partner?
AUD/JPY Divergence: Aussie Service Boom Contrasts with Japan's Fiscal "Truss Moment"
Eurozone Economy Stalls as Demand Evaporates
Nigeria Outlook: FX Stability Critical to Growth as Fiscal Revenue Surges
The Warsh Dilemma: Why the New Fed Nominee Puts Fiscal Plans at Risk
Rate Calc
